249 Downloads Updated 1 year ago
Salamandra is a highly multilingual model pre-trained from scratch that comes in three different sizes — 2B, 7B, and 40B parameters — in base and instruction-tuned variants.
Models
View all →Name
13 models
salamandra:2b_IQ3_M
1.9GB · 8K context window · Text · 1 year ago
salamandra:2b_Q3_K_L
1.9GB · 8K context window · Text · 1 year ago
salamandra:2b_Q4_K_S
2.1GB · 8K context window · Text · 1 year ago
salamandra:2b_Q5_K_M
2.3GB · 8K context window · Text · 1 year ago
salamandra:2b_Q6_K
2.5GB · 8K context window · Text · 1 year ago
salamandra:2b_bf16
4.5GB · 8K context window · Text · 1 year ago
salamandra:2b-instruct_bf16
4.5GB · 8K context window · Text · 1 year ago
salamandra:2b-instruct_IQ3_M
1.9GB · 8K context window · Text · 1 year ago
salamandra:2b-instruct_IQ4_XS
2.0GB · 8K context window · Text · 1 year ago
salamandra:2b-instruct_Q3_K_L
1.9GB · 8K context window · Text · 1 year ago
salamandra:2b-instruct_Q4_K_S
2.1GB · 8K context window · Text · 1 year ago
salamandra:2b-instruct_Q5_K_M
2.3GB · 8K context window · Text · 1 year ago
salamandra:2b-instruct_Q6_K
2.5GB · 8K context window · Text · 1 year ago
Readme

Quantization Details
Both the 2B Base and 2B Instruct models were quantized using llama.cpp with a similar importance matrix calculated from 34 languages (1000 samples each) using the OSCAR dataset. Here we combine the details of quantization types for both models and provide a comparison of their perplexity (PPL) values, file sizes, and notes on each quantization scheme.
2b Quantization Summary
The selection was driven by achieving the lowest possible perplexity while reducing model file size. Quantization types below Q4 were experimented with, but Q4 and above provide the best performance-to-size ratio. The recommended quantizations span IQ3_M to Q6_K, covering a variety of sizes for different use cases.
Perplexity Comparison Table
| Quantization Type | ln(PPL(Q)/PPL(bf16)) (Base) | ln(PPL(Q)/PPL(bf16)) (Instruct) | File Size (G) | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| IQ3_M | 0.079131 | 0.086769 | 1.7 | Good size efficiency, recommended for sub-2GB applications |
| Q3_K_L | 0.068875 | 0.070705 | 1.8 | Slightly larger file size than IQ3_M, modest PPL increase |
| IQ4_XS | - | 0.036968 | 1.8 | Greater size reduction than Q4_K_S, minimal PPL increase (recommended - 2b-instruct) |
| Q4_K_S | 0.027442 | 0.035431 | 1.9 | Minimal PPL impact with a good size reduction (recommended) |
| Q5_K_M | 0.006162 | 0.006139 | 2.2 | Best balance of size and PPL (recommended) |
| Q6_K | 0.001736 | 0.001053 | 2.4 | Nearly lossless performance with reduced size |
| bf16 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 4.2 | Baseline |
Notes on Quantization Selection:
Recommended Quantizations:
- IQ4_XS (2b Instruct): Offers a good size reduction with minimal PPL increase. File size remains very close to Q4_K_S at 1.8GB.
- Q4_K_S: Strong size-to-performance ratio for both models, providing minimal PPL increase while maintaining a small size.
- Q5_K_M: Excellent balance between low perplexity and a modest file size, recommended for most applications.
Non-recommended Quantizations:
- IQ3_M: The best of the highly compressed quantizations, offering good size efficiency with a manageable PPL increase. Suitable for sub-2GB requirements.
- Q3_K_L: Modest PPL increase but provides a slightly larger file size compared to IQ3_M.
- Q6_K: Delivers nearly bf16 performance with significantly smaller file size. Suitable for those needing near-lossless accuracy.
Observations on Differences:
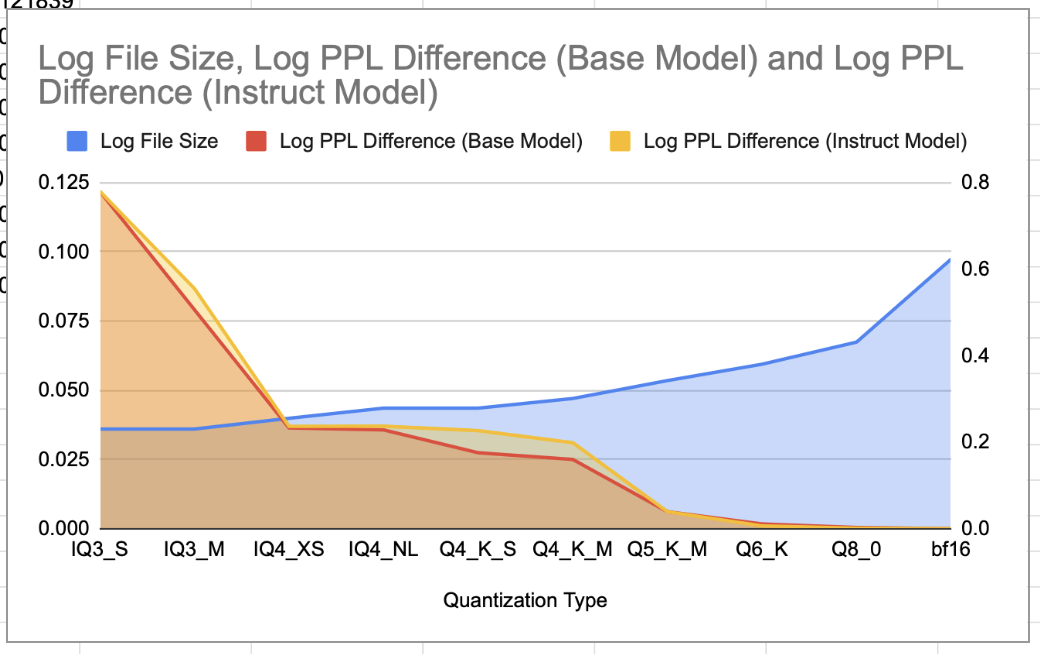
- The 2B Instruct model shows a slight upward shift in PPL values across quantization types compared to the 2B Base model. This is likely due to the additional instruction-tuning step, which introduces slightly higher loss.
- Despite these differences, the overall pattern of quantization performance remains consistent across both models, reinforcing the reliability of these schemes irrespective of fine-tuning.
Defending the Selection:
Diversity in Quantization Types:
- I Quantization Below Q4: IQ3_M offers a solid sub-Q4 option for highly compressed models with a good size-to-performance trade-off.
- K Quantization At and Above Q4: Q4_K_S, Q5_K_M, and Q6_K offer a range of options with strong PPL performance and reduced file sizes.
Selection Criteria:
- Log PPL Difference <0.3: Only models with a log PPL difference of less than 0.3 are included to ensure acceptable performance even in highly quantized forms.
- No Redundancy in File Size: Each quantization is chosen to provide unique value without overlap in file sizes and performance, ensuring a comprehensive but concise selection.
- For 2B Base: In an effort to achieve a model under 1.5GB, we attempted quantizing with IQ2_XS. However, the resulting file size slightly exceeded this target, and the perplexity was significantly higher than acceptable (more than double the 0.3 selection threshold). For models under 1.7GB, Richard Erkhov’s static quantizations are a better option as they don’t use the importance matrix, resulting in smaller sizes.
- For 2B Instruct: An attempt to reduce the file size even further below IQ3_M was made with IQ2_M, but the perplexity remained unacceptable and exceeded the log PPL difference threshold of 0.3. As with the base model, those needing a model smaller than 1.7GB might prefer Richard Erkhov’s static quantizations, which sacrifice the importance matrix for size reduction.
PPL is measured (with llama-perplexity) from a sample of 50 of each language from the same dataset used to calculate the importance matrix.
Salamandra Model Card
Salamandra is a highly multilingual model pre-trained from scratch that comes in three different sizes — 2B, 7B, and 40B parameters — with their respective base and instruction-tuned variants. This model card corresponds to the 7B instructed and base versions.
The entire Salamandra family is released under a permissive Apache 2.0 license. Along with the open weights, all training scripts and configuration files are made publicly available in this GitHub repository.
[!WARNING] DISCLAIMER: This warning applies to the 2B-instruct version. The model is a first proof-of-concept designed to demonstrate the instruction-following capabilities of recently released base models. It has been optimized to engage in conversation but has NOT been aligned through RLHF to filter or avoid sensitive topics. As a result, it may generate harmful or inappropriate content. The team is actively working to enhance its performance through further instruction and alignment with RL techniques.
Model Details (2B Version)
Description
Transformer-based decoder-only language model that has been pre-trained from scratch on 7.8 trillion tokens of highly curated data. The pre-training corpus contains text in 35 European languages and code.
Hyperparameters
The full list of hyperparameters for each model can be found here.
Architecture
| Total Parameters | 2,253,490,176 |
| Embedding Parameters | 524,288,000 |
| Layers | 24 |
| Hidden size | 2,048 |
| Attention heads | 16 |
| Context length | 8,192 |
| Vocabulary size | 256,000 |
| Precision | bfloat16 |
| Embedding type | RoPE |
| Activation Function | SwiGLU |
| Layer normalization | RMS Norm |
| Flash attention | ✅ |
| Grouped Query Attention | ❌ |
| Num. query groups | N/A |
Intended Use
Direct Use
The models are intended for both research and commercial use in any of the languages included in the training data. The base models are intended either for language generation or to be further fine-tuned for specific use-cases. The instruction-tuned variants can be used as general-purpose assistants, as long as the user is fully aware of the model’s limitations.
Out-of-scope Use
The model is not intended for malicious activities, such as harming others or violating human rights. Any downstream application must comply with current laws and regulations. Irresponsible usage in production environments without proper risk assessment and mitigation is also discouraged.
Hardware and Software
Training Framework
Pre-training was conducted using NVIDIA’s NeMo Framework, which leverages PyTorch Lightning for efficient model training in highly distributed settings.
The instruction-tuned versions were produced with FastChat.
Compute Infrastructure
All models were trained on MareNostrum 5, a pre-exascale EuroHPC supercomputer hosted and operated by Barcelona Supercomputing Center.
The accelerated partition is composed of 1,120 nodes with the following specifications: - 4x Nvidia Hopper GPUs with 64 HBM2 memory - 2x Intel Sapphire Rapids 8460Y+ at 2.3Ghz and 32c each (64 cores) - 4x NDR200 (BW per node 800Gb/s) - 512 GB of Main memory (DDR5) - 460GB on NVMe storage
| Model | Nodes | GPUs |
|---|---|---|
| 2B | 64 | 256 |
| 7B | 128 | 512 |
| 40B | 256 / 512 | 1,024 / 2,048 |
Data
Pretraining Data
The training corpus consists of 2.4 trillion tokens, including 35 European languages and 92 programming languages. It amounts to a total of 33TB of pre-processed text. Languages were sampled manually by giving x2 oversampling to Spain’s co-official languages (Spanish, Catalan, Galician and Basque), code was undersampled by half, and the rest of the languages were kept as is, resulting in the following distribution:

This highly multilingual corpus is predominantly composed of data from Colossal OSCAR, which contributes a significant 66.06% of the total tokens. Following this, Starcoder provides 11.91%, and Spanish Crawling adds 3.34%. The next largest sources are French FR at 3.12% and Proof Pile at 1.98%. Other notable contributions include Macocu, Pile of Law, and Eurlex, each contributing around 1.5% to 1.3%. These major sources collectively form the bulk of the corpus, ensuring a rich and diverse dataset for training the language model. The remaining 10% comes from smaller sources in various languages.
Feel free to click the expand button below to see the full list of sources.
Data Sources
| Dataset | Language | Source | |-----------------------------------------------|---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------| | Parlamint corpus | at, bg, cz, dk, ee, es, es-ga, fi, fr, gb, gr, hr, hu, it, lv, nl, no, pl, pt, rs, se, si | Erjavec et al., 2021 | | Bulgarian National Corpus | bg | [Link](http://old.dcl.bas.bg/dataset/BulNC.7z) | | Crawl of Bulgarian news websites | bg | [Link](http://old.dcl.bas.bg/dataset/Bulgarian_news.7z) | | Colossal OSCAR 1.0 | bg, ca, cs, cy, da, de, el, en, es, et, eu, fi, fr, ga, gl, hr, hu, it, lt, lv, mt, nl, nn, no, oc, pl, pt, ro, ru, sh, sk, sl, sr, sv, uk | Brack et al., 2024 | | Wikimedia dumps | bg, ca, cs, da, de, el, en, es, et, eu, fi, fr, ga, gl, hr, hu, it, lt, lv, mt, nl, nn, no, pl, pt, ro, sh, sk, sl, sr, uk | [Link](https://dumps.wikimedia.org/) | | OpenSubtitlesv2016 | bg, ca, cs, da, de, el, en, es, et, eu, fi, fr, gl, hr, it, lt, lv, nl, no, pl, pt, ro, sk, sl, sr, sv, uk | Lison & Tiedemann, 2016 | | MaCoCu web corpus | bg, ca, el, hr, mt, sl, sr, uk | Bañón et al., 2022 | | EurLEX-Resources | bg, cs, da, de, el, en, es, et, fi, fr, ga, hr, hu, it, lt, lv, mt, nl, pl, pt, ro, sk, sl, sv | [Link](https://huggingface.co/datasets/joelniklaus/eurlex_resources) | | MC4-Legal | bg, cs, da, de, el, en, es, et, fi, fr, ga, hu, it, lt, lv, mt, nl, pl, pt, ro, sk, sl, sv | [Link](https://huggingface.co/datasets/joelito/legal-mc4) | | CURLICAT Corpus | bg, hr, hu, pl, ro, sk, sl | Váradi et al., 2022 | | CATalog | ca | Palomar-Giner et al., 2024 | | Spanish Crawling | ca, es, eu, gl | Relevant Spanish websites crawling | | Starcoder | code | Li et al., 2023 | | SYN v9: large corpus of written Czech | cs | Křen et al., 2021 | | Welsh-GOV | cy | Crawling from [Link](https://www.llyw.cymru) | | DaNewsroom | da | Varab & Schluter, 2020 | | Danish GigaWord | da | Strømberg-Derczynski et al., 2021 | | DK-CLARIN Reference Corpus of General Danish | da | [Link](https://korpus.dsl.dk/clarin/) | | The Danish Parliament Corpus 2009 - 2017, v1 | da | Hansen, 2018 | | DeWaC | de | [Link](https://docs.sslmit.unibo.it/doku.php?id=corpora:dewac) | | Open Legal Data - German court decisions and laws | de | Ostendorff et al., 2020 | | Greek Legal Code | el | Papaloukas et al., 2021 | | Greek Web Corpus | el | Outsios et al., 2018 | | Auxiliary Mathematics Problems and Solutions (AMPS) dataset | en | Hendrycks et al., 2021 | | BIGPATENT | en | Sharma et al., 2019 | | FineWeb-Edu (350BT subset) | en | Penedo et al., 2024 | | peS2o | en | Soldaini & Lo, 2023 | | PG-19 | en | Rae et al., 2019 | | Pile of Law (selected subsets) | en | Henderson* et al., 2022 | | proof-pile | en | [Link](https://huggingface.co/datasets/hoskinson-center/proof-pile) | | RedPajama-Data T1 (StackExchange subset) | en | Computer, 2023 | | The Pile (PhilPapers subset) | en | Gao et al., 2021 | | Biomedical | es | Internally generated scientific dataset: Dialnet, Scielo, CSIC, TDX, BSC, UCM | | HPLTDatasets v1 - Spanish | es | de Gibert et al., 2024 | | Legal | es | Internally generated legal dataset: BOE, BORME, Senado, Congreso, Spanish court orders, DOGC | | Scientific | es | Internally generated scientific dataset: Wikipedia LS, Pubmed, MeSpEn, patents, clinical cases, medical crawler | | Spanish Legal Domain Corpora | es | Gutiérrez-Fandiño et al., 2021 | | Estonian National Corpus 2021 | et | Koppel & Kallas, 2022 | | Estonian Reference Corpus | et | [Link](https://www.cl.ut.ee/korpused/segakorpus/) | | EusCrawl (w/o Wikipedia or NC-licenses) | eu | Artetxe et al., 2022 | | Latxa Corpus v1.1 | eu | Etxaniz et al., 2024 [Link](https://huggingface.co/datasets/HiTZ/latxa-corpus-v1.1) | | Aya Dataset (w/o Evaluation Suite) | eu, hr, nl, fi, ka, hu, lt, nn, ro, sk, lv, cy, bg, cs, en, fr, de, ga, mt, pl, ru, sl, sv, ca, da, et, gl, el, it, no, pt, sr, es, uk | Singh et al., 2024 | | Yle Finnish News Archive | fi | [Link](http://urn.fi/urn:nbn:fi:lb-2021050401) | | CaBeRnet: a New French Balanced Reference Corpus | fr | Popa-Fabre et al., 2020 | | French Public Domain Books | fr | [Link](https://huggingface.co/datasets/PleIAs/French-PD-Books) | | French Public Domain Newspapers | fr | [Link](https://huggingface.co/datasets/PleIAs/French-PD-Newspapers) | | Irish Universal Dependencies | ga | [Link](https://universaldependencies.org/ga/index.html) | | The Gaois bilingual corpus of English-Irish legislation (Irish legislation) | ga | [Link](https://portulanclarin.net/repository/browse/the-gaois-bilingual-corpus-of-english-irish-legislation-processed/daeac17c9e3511ea9b7f02420a000407b83de243dc0b469aab41084386c5b80f/) | | CorpusNÓS | gl | de-Dios-Flores et al., 2024 | | Croatian web corpus hrWaC 2.1 | hr | Ljubešić & Klubička, 2014 | | ITWaC | it | [Link](https://docs.sslmit.unibo.it/doku.php?id=corpora:itwac) | | Corpus of State-related content from the Latvian Web (Processed) | lv | [Link](https://catalog.elra.info/en-us/repository/browse/ELRA-W0169/) | | Korpus Malti | mt | Micallef et al., 2022 | | SoNaR Corpus NC 1.2 | nl | [Link](https://taalmaterialen.ivdnt.org/download/tstc-sonar-corpus/) | | Norwegian Colossal Corpus | nn, no | Kummervold et al., 2021 | | Occitan Corpus | oc | Provided by [IEA](https://www.institutestudisaranesi.cat/) | | NKJP-PodkorpusMilionowy-1.2 (National Corpus of Polish) | pl | Lewandowska-Tomaszczyk et al., 2013 | | Polish Parliamentary Corpus / Korpus Dyskursu Parlamentarnego | pl | Ogrodniczuk, 2018 | | Brazilian Portuguese Web as Corpus | pt | Wagner Filho et al., 2018 | | ParlamentoPT | pt | Rodrigues et al., 2023 | | MARCELL Romanian legislative subcorpus v2 | ro | [Link](https://elrc-share.eu/reposMARCELL%20Romanian%20legislative%20subcorpus%20v2itory/browse/marcell-romanian-legislative-subcorpus-v2/2da548428b9d11eb9c1a00155d026706ce94a6b59ffc4b0e9fb5cd9cebe6889e/) | | Korpus slovenských právnych predpisov v1.9 | sk | [Link](https://www.juls.savba.sk/data/marcell/legal-sk-20220322-1.9.ver.xz) | | od-justice 2.0 | sk | [Link](https://www.juls.savba.sk/data/od-justice/od-justice-2.0.ver.xz) | | Corpus of academic Slovene KAS 2.0 | sl | Žagar et al., 2022 | | slWaC web corpus | sl | Erjavec et al., 2015 | | SrpKorSubset (news, legal, academic, conversation, literary) | sr | [Link](http://www.korpus.matf.bg.ac.rs/) | | The Swedish Culturomics Gigaword Corpus | sv | Rødven-Eide, 2016 | | Corpus of laws and legal acts of Ukraine | uk | [Link](https://lang.org.ua/en/corpora/#anchor7) |References
- Abadji, J., Suárez, P. J. O., Romary, L., & Sagot, B. (2021). Ungoliant: An optimized pipeline for the generation of a very large-scale multilingual web corpus (H. Lüngen, M. Kupietz, P. Bański, A. Barbaresi, S. Clematide, & I. Pisetta, Eds.; pp. 1–9). Leibniz-Institut für Deutsche Sprache. [Link](https://doi.org/10.14618/ids-pub-10468) - Artetxe, M., Aldabe, I., Agerri, R., Perez-de-Viñaspre, O., & Soroa, A. (2022). Does Corpus Quality Really Matter for Low-Resource Languages? - Bañón, M., Esplà-Gomis, M., Forcada, M. L., García-Romero, C., Kuzman, T., Ljubešić, N., van Noord, R., Sempere, L. P., Ramírez-Sánchez, G., Rupnik, P., Suchomel, V., Toral, A., van der Werff, T., & Zaragoza, J. (2022). MaCoCu: Massive collection and curation of monolingual and bilingual data: Focus on under-resourced languages. Proceedings of the 23rd Annual Conference of the European Association for Machine Translation, 303–304. [Link](https://aclanthology.org/2022.eamt-1.41) - Brack, M., Ostendorff, M., Suarez, P. O., Saiz, J. J., Castilla, I. L., Palomar-Giner, J., Shvets, A., Schramowski, P., Rehm, G., Villegas, M., & Kersting, K. (2024). Community OSCAR: A Community Effort for Multilingual Web Data. [Link](https://occiglot.eu/papers/Community_Oscar.pdf) - Computer, T. (2023). RedPajama: An Open Source Recipe to Reproduce LLaMA training dataset [Computer software]. [Link](https://github.com/togethercomputer/RedPajama-Data) - de Gibert, O., Nail, G., Arefyev, N., Bañón, M., van der Linde, J., Ji, S., Zaragoza-Bernabeu, J., Aulamo, M., Ramírez-Sánchez, G., Kutuzov, A., Pyysalo, S., Oepen, S., & Tiedemann, J. (2024). A New Massive Multilingual Dataset for High-Performance Language Technologies (arXiv:2403.14009). arXiv. [Link](http://arxiv.org/abs/2403.14009) - Dodge, J., Sap, M., Marasović, A., Agnew, W., Ilharco, G., Groeneveld, D., Mitchell, M., & Gardner, M. (2021). Documenting Large Webtext Corpora: A Case Study on the Colossal Clean Crawled Corpus. In M.-F. Moens, X. Huang, L. Specia, & S. W. Yih (Eds.), Proceedings of the 2021 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing (pp. 1286–1305). Association for Computational Linguistics. [Link](https://doi.org/10.18653/v1/2021.emnlp-main.98) - Erjavec, T., Ljubešić, N., & Logar, N. (2015). The slWaC corpus of the Slovene web. Informatica (Slovenia), 39, 35–42. - Erjavec, T., Ogrodniczuk, M., Osenova, P., Ljubešić, N., Simov, K., Grigorova, V., Rudolf, M., Pančur, A., Kopp, M., Barkarson, S., Steingrímsson, S. hór, van der Pol, H., Depoorter, G., de Does, J., Jongejan, B., Haltrup Hansen, D., Navarretta, C., Calzada Pérez, M., de Macedo, L. D., … Rayson, P. (2021). Linguistically annotated multilingual comparable corpora of parliamentary debates ParlaMint.ana 2.1. [Link](http://hdl.handle.net/11356/1431) - Etxaniz, J., Sainz, O., Perez, N., Aldabe, I., Rigau, G., Agirre, E., Ormazabal, A., Artetxe, M., & Soroa, A. (2024). Latxa: An Open Language Model and Evaluation Suite for Basque. [Link] (https://arxiv.org/abs/2403.20266) - Gao, L., Biderman, S., Black, S., Golding, L., Hoppe, T., Foster, C., Phang, J., He, H., Thite, A., Nabeshima, N., Presser, S., & Leahy, C. (2021). The Pile: An 800GB Dataset of Diverse Text for Language Modeling. CoRR, abs/2101.00027. [Link](https://arxiv.org/abs/2101.00027) - Gutiérrez-Fandiño, A., Armengol-Estapé, J., Gonzalez-Agirre, A., & Villegas, M. (2021). Spanish Legalese Language Model and Corpora. - Hansen, D. H. (2018). The Danish Parliament Corpus 2009—2017, v1. [Link](http://hdl.handle.net/20.500.12115/8) - Henderson*, P., Krass*, M. S., Zheng, L., Guha, N., Manning, C. D., Jurafsky, D., & Ho, D. E. (2022). Pile of Law: Learning Responsible Data Filtering from the Law and a 256GB Open-Source Legal Dataset. arXiv. [Link](https://arxiv.org/abs/2207.00220) - Hendrycks, D., Burns, C., Kadavath, S., Arora, A., Basart, S., Tang, E., Song, D., & Steinhardt, J. (2021). Measuring Mathematical Problem Solving With the MATH Dataset. NeurIPS. - Jansen, T., Tong, Y., Zevallos, V., & Suarez, P. O. (2022). Perplexed by Quality: A Perplexity-based Method for Adult and Harmful Content Detection in Multilingual Heterogeneous Web Data. - Koppel, K., & Kallas, J. (2022). Eesti keele ühendkorpuste sari 2013–2021: Mahukaim eestikeelsete digitekstide kogu. Eesti Rakenduslingvistika Ühingu Aastaraamat Estonian Papers in Applied Linguistics, 18, 207–228. [Link](https://doi.org/10.5128/erya18.12) - Křen, M., Cvrček, V., Henyš, J., Hnátková, M., Jelínek, T., Kocek, J., Kováříková, D., Křivan, J., Milička, J., Petkevič, V., Procházka, P., Skoumalová, H., Šindlerová, J., & Škrabal, M. (2021). SYN v9: Large corpus of written Czech. [Link](http://hdl.handle.net/11234/1-4635) - Kreutzer, J., Caswell, I., Wang, L., Wahab, A., van Esch, D., Ulzii-Orshikh, N., Tapo, A., Subramani, N., Sokolov, A., Sikasote, C., Setyawan, M., Sarin, S., Samb, S., Sagot, B., Rivera, C., Rios, A., Papadimitriou, I., Osei, S., Suarez, P. O., … Adeyemi, M. (2022). Quality at a Glance: An Audit of Web-Crawled Multilingual Datasets. Transactions of the Association for Computational Linguistics, 10, 50–72. [Link](https://doi.org/10.1162/tacl_a_00447) - Kummervold, P. E., De la Rosa, J., Wetjen, F., & Brygfjeld, S. A. (2021). Operationalizing a National Digital Library: The Case for a Norwegian Transformer Model. In S. Dobnik & L. Øvrelid (Eds.), Proceedings of the 23rd Nordic Conference on Computational Linguistics (NoDaLiDa) (pp. 20–29). Linköping University Electronic Press, Sweden. [Link](https://aclanthology.org/2021.nodalida-main.3) - Lewandowska-Tomaszczyk, B., Górski, R., Łaziński, M., & Przepiórkowski, A. (2013). The National Corpus of Polish (NKJP). Language use and data analysis. 309–319. - Li, R., Allal, L. B., Zi, Y., Muennighoff, N., Kocetkov, D., Mou, C., Marone, M., Akiki, C., Li, J., Chim, J., Liu, Q., Zheltonozhskii, E., Zhuo, T. Y., Wang, T., Dehaene, O., Davaadorj, M., Lamy-Poirier, J., Monteiro, J., Shliazhko, O., … Vries, H. de. (2023). StarCoder: May the source be with you! - Lison, P., & Tiedemann, J. (2016). OpenSubtitles2016: Extracting Large Parallel Corpora from Movie and TV Subtitles. In N. Calzolari, K. Choukri, T. Declerck, S. Goggi, M. Grobelnik, B. Maegaard, J. Mariani, H. Mazo, A. Moreno, J. Odijk, & S. Piperidis (Eds.), Proceedings of the Tenth International Conference on Language Resources and Evaluation (LREC’16) (pp. 923–929). European Language Resources Association (ELRA). [Link](https://aclanthology.org/L16-1147) - Ljubešić, N., & Klubička, F. (2014). Bs,hr,srWaC - Web Corpora of Bosnian, Croatian and Serbian. In F. Bildhauer & R. Schäfer (Eds.), Proceedings of the 9th Web as Corpus Workshop (WaC-9) (pp. 29–35). Association for Computational Linguistics. [Link](https://doi.org/10.3115/v1/W14-0405) - Micallef, K., Gatt, A., Tanti, M., van der Plas, L., & Borg, C. (2022). Pre-training Data Quality and Quantity for a Low-Resource Language: New Corpus and BERT Models for Maltese. Proceedings of the Third Workshop on Deep Learning for Low-Resource Natural Language Processing, 90–101. [Link](https://doi.org/10.18653/v1/2022.deeplo-1.10) - Ogrodniczuk, M. (2018). Polish Parliamentary Corpus. [Link](https://api.semanticscholar.org/CorpusID:235134113) - Ostendorff, M., Blume, T., & Ostendorff, S. (2020). Towards an Open Platform for Legal Information. Proceedings of the ACM/IEEE Joint Conference on Digital Libraries in 2020, 385–388. [Link](https://doi.org/10.1145/3383583.3398616) - Ostendorff, M., Suarez, P. O., Lage, L. F., & Rehm, G. (2024). LLM-Datasets: An Open Framework for Pretraining Datasets of Large Language Models. First Conference on Language Modeling. [Link](https://openreview.net/forum?id=5RdIMlGLXL) - Outsios, S., Skianis, K., Meladianos, P., Xypolopoulos, C., & Vazirgiannis, M. (2018). Word Embeddings from Large-Scale Greek Web content. arXiv Preprint arXiv:1810.06694. - Palomar-Giner, J., Saiz, J. J., Espuña, F., Mina, M., Da Dalt, S., Llop, J., Ostendorff, M., Ortiz Suarez, P., Rehm, G., Gonzalez-Agirre, A., & Villegas, M. (2024). A CURATEd CATalog: Rethinking the Extraction of Pretraining Corpora for Mid-Resourced Languages. In N. Calzolari, M.-Y. Kan, V. Hoste, A. Lenci, S. Sakti, & N. Xue (Eds.), Proceedings of the 2024 Joint International Conference on Computational Linguistics, Language Resources and Evaluation (LREC-COLING 2024) (pp. 335–349). ELRA and ICCL. [Link](https://aclanthology.org/2024.lrec-main.31) - Papaloukas, C., Chalkidis, I., Athinaios, K., Pantazi, D.-A., & Koubarakis, M. (2021). Multi-granular Legal Topic Classification on Greek Legislation. Proceedings of the Natural Legal Language Processing Workshop 2021, 63–75. [Link](https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2109.15298) - Popa-Fabre, M., Ortiz Suárez, P. J., Sagot, B., & de la Clergerie, É. (2020). French Contextualized Word-Embeddings with a sip of CaBeRnet: A New French Balanced Reference Corpus. Proceedings of the 8th Workshop on Challenges in the Management of Large Corpora, 15–23. [Link](https://aclanthology.org/2020.cmlc-1.3) - Rae, J. W., Potapenko, A., Jayakumar, S. M., Hillier, C., & Lillicrap, T. P. (2019). Compressive Transformers for Long-Range Sequence Modelling. arXiv Preprint. [Link](https://arxiv.org/abs/1911.05507) - Rodrigues, J., Gomes, L., Silva, J., Branco, A., Santos, R., Cardoso, H. L., & Osório, T. (2023). Advancing Neural Encoding of Portuguese with Transformer Albertina PT-\*. - Rødven-Eide, S. (2016). The Swedish Culturomics Gigaword CorpusThe Swedish Culturomics Gigaword Corpus [Dataset]. Språkbanken Text. [Link](https://doi.org/10.23695/3WMV-1Z09) - Sharma, E., Li, C., & Wang, L. (2019). BIGPATENT: A Large-Scale Dataset for Abstractive and Coherent Summarization. CoRR, abs/1906.03741. [Link](http://arxiv.org/abs/1906.03741) - Soldaini, L., & Lo, K. (2023). peS2o (Pretraining Efficiently on S2ORC) Dataset. Allen Institute for AI. - Strømberg-Derczynski, L., Ciosici, M., Baglini, R., Christiansen, M. H., Dalsgaard, J. A., Fusaroli, R., Henrichsen, P. J., Hvingelby, R., Kirkedal, A., Kjeldsen, A. S., Ladefoged, C., Nielsen, F. Å., Madsen, J., Petersen, M. L., Rystrøm, J. H., & Varab, D. (2021). The Danish Gigaword Corpus. Proceedings of the 23rd Nordic Conference on Computational Linguistics (NoDaLiDa), 413–421. [Link](https://aclanthology.org/2021.nodalida-main.46) - Subramani, N., Luccioni, S., Dodge, J., & Mitchell, M. (2023). Detecting Personal Information in Training Corpora: An Analysis. 208–220. [Link](https://doi.org/10.18653/v1/2023.trustnlp-1.18) - Varab, D., & Schluter, N. (2020). DaNewsroom: A Large-scale Danish Summarisation Dataset. Proceedings of The 12th Language Resources and Evaluation Conference, 6731–6739. [Link](https://www.aclweb.org/anthology/2020.lrec-1.831) - Váradi, T., Nyéki, B., Koeva, S., Tadić, M., Štefanec, V., Ogrodniczuk, M., Nitoń, B., Pezik, P., Barbu Mititelu, V., Irimia, E., Mitrofan, M., Tufi\textcommabelows, D., Garabík, R., Krek, S., & Repar, A. (2022). Introducing the CURLICAT Corpora: Seven-language Domain Specific Annotated Corpora from Curated Sources. In N. Calzolari, F. Béchet, P. Blache, K. Choukri, C. Cieri, T. Declerck, S. Goggi, H. Isahara, B. Maegaard, J. Mariani, H. Mazo, J. Odijk, & S. Piperidis (Eds.), Proceedings of the Thirteenth Language Resources and Evaluation Conference (pp. 100–108). European Language Resources Association. [Link](https://aclanthology.org/2022.lrec-1.11) - Wagner Filho, J. A., Wilkens, R., Idiart, M., & Villavicencio, A. (2018). The brwac corpus: A new open resource for brazilian portuguese. Proceedings of the Eleventh International Conference on Language Resources and Evaluation (LREC 2018). - Žagar, A., Kavaš, M., Robnik-Šikonja, M., Erjavec, T., Fišer, D., Ljubešić, N., Ferme, M., Borovič, M., Boškovič, B., Ojsteršek, M., & Hrovat, G. (2022). Corpus of academic Slovene KAS 2.0. [Link](http://hdl.handle.net/11356/1448) - Alicia Parrish, Angelica Chen, Nikita Nangia, Vishakh Padmakumar, Jason Phang, Jana Thompson, Phu Mon Htut, and Samuel Bowman. 2022. BBQ: A hand-built bias benchmark for question answering. In Findings of the Association for Computational Linguistics: ACL 2022, pages 2086–2105, Dublin, Ireland. Association for Computational Linguistics. - Emily Sheng, Kai-Wei Chang, Premkumar Natarajan, and Nanyun Peng. 2019. The Woman Worked as a Babysitter: On Biases in Language Generation. In Proceedings of the 2019 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing and the 9th International Joint Conference on Natural Language Processing (EMNLP-IJCNLP), pages 3407–3412, Hong Kong, China. Association for Computational Linguistics. - Clark, P., Cowhey, I., Etzioni, O., Khot, T., Sabharwal, A., Schoenick, C., & Tafjord, O. (2018). Think you have Solved Question Answering? Try ARC, the AI2 Reasoning Challenge. arXiv:1803. 05457v1. - Richard Socher, Alex Perelygin, Jean Wu, Jason Chuang, Christopher D. Manning, Andrew Ng, and Christopher Potts. 2013. Recursive Deep Models for Semantic Compositionality Over a Sentiment Treebank. In Proceedings of the 2013 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing, pages 1631–1642, Seattle, Washington, USA. Association for Computational Linguistics. - Penedo, G., Kydlíček, H., allal, L. B., Lozhkov, A., Mitchell, M., Raffel, C., Von Werra, L., & Wolf, T. (2024). The FineWeb Datasets: Decanting the Web for the Finest Text Data at Scale (arXiv:2406.17557). arXiv. http://arxiv.org/abs/2406.17557 - Singh, S., Vargus, F., Dsouza, D., Karlsson, B. F., Mahendiran, A., Ko, W.-Y., Shandilya, H., Patel, J., Mataciunas, D., OMahony, L., Zhang, M., Hettiarachchi, R., Wilson, J., Machado, M., Moura, L. S., Krzemiński, D., Fadaei, H., Ergün, I., Okoh, I., … Hooker, S. (2024). Aya Dataset: An Open-Access Collection for Multilingual Instruction Tuning (arXiv:2402.06619). arXiv. http://arxiv.org/abs/2402.06619The model was trained for 3 epochs, with two final rounds of 0.3B higher-quality tokens each, meaning that the total number of tokens seen during pre-training amounts to roughly 7.8 trillion tokens.
We provide an extense Datasheet section following the best practices defined by (Gebru et al., 2021).
Datasheet
#### Motivation **For what purpose was the dataset created? Was there a specific task in mind? Was there a specific gap that needed to be filled? Please provide a description.** The purpose of creating this dataset is to pre-train the Salamandra family of multilingual models with high performance in a large number of European languages (35) and code (including 92 different programming languages). In addition, we aim to represent especially the co-official languages of Spain: Spanish, Catalan, Galician, and Basque. This is the reason why we carry out an oversampling of these languages. We detected that there is a great lack of massive multilingual data, especially in minority languages (Ostendorff & Rehm, 2023), so part of our efforts in the creation of this pre-training dataset have resulted in the contribution to large projects such as the Community OSCAR (Brack et al., 2024), which includes 151 languages and 40T words, or CATalog (Palomar-Giner et al., 2024), the largest open dataset in Catalan in the world. **Who created the dataset (e.g., which team, research group) and on behalf of which entity (e.g., company, institution, organization)?** The dataset has been created by the Language Technologies unit (LangTech) of the Barcelona Supercomputing Center - Centro Nacional de Supercomputación (BSC-CNS), which aims to advance the field of natural language processing through cutting-edge research and development and the use of HPC. In particular, it was created by the unit's data team, the main contributors being Javier Saiz, Ferran Espuña, and Jorge Palomar. However, the creation of the dataset would not have been possible without the collaboration of a large number of collaborators, partners, and public institutions, which can be found in detail in the acknowledgements. **Who funded the creation of the dataset? If there is an associated grant, please provide the name of the grantor and the grant name and number.** This work/research has been promoted and financed by the Government of Catalonia through the [Aina project](https://projecteaina.cat/). #### Composition **What do the instances that comprise the dataset represent (e.g., documents, photos, people, countries)? Are there multiple types of instances (e.g., movies, users, and ratings; people and interactions between them; nodes and edges)? Please provide a description.** The dataset consists entirely of text documents in various languages. Specifically, data was mainly sourced from the following databases and repositories: - **Common Crawl:** Repository that holds website data and is run by the Common Crawl non-profit organization. It is updated monthly and is distributed under the CC0 1.0 public domain license. - **GitHub:** Community platform that allows developers to create, store, manage, and share their code. Repositories are crawled and then distributed with their original licenses, which may vary from permissive to non-commercial licenses. - **Wikimedia:** Database that holds the collection databases managed by the Wikimedia Foundation, including Wikipedia, Wikibooks, Wikinews, Wikiquote, Wikisource, and Wikivoyage. It is updated monthly and is distributed under Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License 4.0. - **EurLex:** Repository that holds the collection of legal documents from the European Union, available in all of the EU’s 24 official languages and run by the Publications Office of the European Union. It is updated daily and is distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International license. - **Other repositories:** Specific repositories were crawled under permission for domain-specific corpora, which include academic, legal, and newspaper repositories. We provide a complete list of dataset sources at the end of this section. **How many instances are there in total (of each type, if appropriate)?** The dataset contains a diverse range of instances across multiple languages, with notable adjustments for certain languages. English represents the largest portion, accounting for 39.08% of the total data. Spanish was upsampled by a factor of 2, bringing its share to 16.59%, while Catalan (1.84%), Basque (0.26%), and Galician (0.36%) were also upsampled by 2. On the other hand, code-related data was downsampled by half, making up 6.42% of the total. Other prominent languages include French (6.59%), Russian (5.39%), German (4.25%), and Hungarian (3.93%), with several additional languages contributing between 1% and 2%, and smaller portions represented by a variety of others. **Does the dataset contain all possible instances or is it a sample (not necessarily random) of instances from a larger set? If the dataset is a sample, then what is the larger set? Is the sample representative of the larger set (e.g., geographic coverage)? If so, please describe how this representativeness was validated/verified. If it is not representative of the larger set, please describe why not (e.g., to cover a more diverse range of instances, because instances were withheld or unavailable).** The dataset is a sample from multiple sources, with different weights based on the primary language of the content: Spanish, Catalan, Basque, and Galician content was upsampled by a factor of two, while programming languages were downsampled by a factor of half. Other sources were sampled in proportion to their occurrence. **What data does each instance consist of? “Raw” data (e.g., unprocessed text or images) or features? In either case, please provide a description.** Each instance consists of a text document processed for deduplication, language identification, and source-specific filtering. Some documents required optical character recognition (OCR) to extract text from non-text formats such as PDFs. **Is there a label or target associated with each instance? If so, please provide a description.** Each instance is labeled with a unique identifier, the primary language of the content, and the URL for web-sourced instances. Additional labels were automatically assigned to detect specific types of content —harmful or toxic content— and to assign preliminary indicators of undesired qualities —very short documents, high density of symbols, etc.— which were used for filtering instances. **Is any information missing from individual instances? If so, please provide a description, explaining why this information is missing (e.g., because it was unavailable). This does not include intentionally removed information, but might include, e.g., redacted text.** No significant information is missing from the instances. **Are relationships between individual instances made explicit (e.g., users’ movie ratings, social network links)? If so, please describe how these relationships are made explicit.** Instances are related through shared metadata, such as source and language identifiers. **Are there recommended data splits (e.g., training, development/validation, testing)? If so, please provide a description of these splits, explaining the rationale behind them.** The dataset is split randomly into training, validation, and test sets. **Are there any errors, sources of noise, or redundancies in the dataset? If so, please provide a description.** Despite removing duplicated instances within each source, redundancy remains at the paragraph and sentence levels, particularly in web-sourced instances where SEO techniques and templates contribute to repeated textual patterns. Some instances may also be duplicated across sources due to format variations. **Is the dataset self-contained, or does it link to or otherwise rely on external resources (e.g., websites, tweets, other datasets)? If it links to or relies on external resources, a) are there guarantees that they will exist, and remain constant, over time; b) are there official archival versions of the complete dataset (i.e., including the external resources as they existed at the time the dataset was created); c) are there any restrictions (e.g., licenses, fees) associated with any of the external resources that might apply to a dataset consumer? Please provide descriptions of all external resources and any restrictions associated with them, as well as links or other access points, as appropriate.** The dataset is self-contained and does not rely on external resources. **Does the dataset contain data that might be considered confidential (e.g., data that is protected by legal privilege or by doctor–patient confidentiality, data that includes the content of individuals’ non-public communications)? If so, please provide a description.** The dataset does not contain confidential data. **Does the dataset contain data that, if viewed directly, might be offensive, insulting, threatening, or might otherwise cause anxiety? If so, please describe why. If the dataset does not relate to people, you may skip the remaining questions in this section.** The dataset includes web-crawled content, which may overrepresent pornographic material across languages (Kreutzer et al., 2022). Although pre-processing techniques were applied to mitigate offensive content, the heterogeneity and scale of web-sourced data make exhaustive filtering challenging, which makes it next to impossible to identify all adult content without falling into excessive filtering, which may negatively influence certain demographic groups (Dodge et al., 2021). **Does the dataset identify any subpopulations (e.g., by age, gender)? If so, please describe how these subpopulations are identified and provide a description of their respective distributions within the dataset.** The dataset does not explicitly identify any subpopulations. **Is it possible to identify individuals (i.e., one or more natural persons), either directly or indirectly (i.e., in combination with other data) from the dataset? If so, please describe how.** Web-sourced instances in the dataset may contain personally identifiable information (PII) that is publicly available on the Web, such as names, IP addresses, email addresses, and phone numbers. While it would be possible to indirectly identify individuals through the combination of multiple data points, the nature and scale of web data makes it difficult to parse such information. In any case, efforts are made to filter or anonymize sensitive data during pre-processing, but some identifiable information may remain in the dataset. **Does the dataset contain data that might be considered sensitive in any way? If so, please provide a description.** Given that the dataset includes web-sourced content and other publicly available documents, instances may inadvertently reveal financial information, health-related details, or forms of government identification, such as social security numbers (Subramani et al., 2023), especially if the content originates from less-regulated sources or user-generated platforms. #### Collection Process **How was the data collected?** This dataset is constituted by combining several sources, whose acquisition methods can be classified into three groups: - Web-sourced datasets with some preprocessing available under permissive license (p.e. Common Crawl). - Domain-specific or language-specific raw crawls (p.e. Spanish Crawling). - Manually curated data obtained through collaborators, data providers (by means of legal assignment agreements) or open source projects (p.e. CATalog). **What mechanisms or procedures were used to collect the data? How were these mechanisms or procedures validated?** According to the three groups previously defined, these are the mechanisms used in each of them: - Open direct download. Validation: data integrity tests. - Ad-hoc scrapers or crawlers. Validation: software unit and data integrity tests. - Direct download via FTP, SFTP, API or S3. Validation: data integrity tests. **If the dataset is a sample from a larger set, what was the sampling strategy?** The sampling strategy was to use the whole dataset resulting from the filtering explained in the ‘preprocessing/cleaning/labelling’ section, with the particularity that an upsampling of 2 (i.e. twice the probability of sampling a document) was performed for the co-official languages of Spain (Spanish, Catalan, Galician, Basque), and a downsampling of 1/2 was applied for code (half the probability of sampling a code document, evenly distributed among all programming languages). **Who was involved in the data collection process and how were they compensated?** This data is generally extracted, filtered and sampled by automated processes. The code required to run these processes has been developed entirely by members of the LangTech data team, or otherwise obtained from open-source software. Furthermore, there has been no monetary consideration for acquiring data from suppliers. **Over what timeframe was the data collected? Does this timeframe match the creation timeframe of the data associated with the instances? If not, please describe the timeframe in which the data associated with the instances was created.** Data were acquired and processed from April 2023 to April 2024. However, as mentioned, much data has been obtained from open projects such as Common Crawl, which contains data from 2014, so it is the end date (04/2024) rather than the start date that is important. **Were any ethical review processes conducted? If so, please provide a description of these review processes, including the outcomes, as well as a link or other access point to any supporting documentation.** No particular ethical review process has been carried out as the data is mostly open and not particularly sensitive. However, we have an internal evaluation team and a bias team to monitor ethical issues. In addition, we work closely with ‘Observatori d'Ètica en Intel·ligència Artificial’ (OEIAC) and ‘Agencia Española de Supervisión de la Inteligencia Artificial’ (AESIA) to audit the processes we carry out from an ethical and legal point of view, respectively. #### Preprocessing **Was any preprocessing/cleaning/labeling of the data done? If so, please provide a description. If not, you may skip the remaining questions in this section.** Instances of text documents were not altered, but web-sourced documents were filtered based on specific criteria along two dimensions: - Quality: documents with a score lower than 0.8, based on undesired qualities, such as documents with low number of lines, very short sentences, presence of long footers and headers, and high percentage of punctuation, obtained through CURATE (Palomar-Giner et al., 2024) were filtered out. - Harmful or adult content: documents originating from Colossal OSCAR were filtered using LLM-Datasets (Ostendorff et al., 2024) based on the perplexity from a language model (‘harmful_pp’ field) provided by the Ungoliant pipeline (Abadji et al., 2021). **Was the “raw” data saved in addition to the preprocessed/cleaned/labeled data? If so, please provide a link or other access point to the “raw” data.** The original raw data was not kept. **Is the software that was used to preprocess/clean/label the data available? If so, please provide a link or other access point.** Yes, the preprocessing and filtering software is open-sourced. The [CURATE](https://github.com/langtech-bsc/CURATE) pipeline was used for Spanish Crawling and CATalog, and the [Ungoliant](https://github.com/oscar-project/ungoliant) pipeline was used for the OSCAR project. #### Uses **Has the dataset been used for any tasks already? If so, please provide a description.** Pre-train the Salamandra model family. **What (other) tasks could the dataset be used for?** The data can be used primarily to pre-train other language models, which can then be used for a wide range of use cases. The dataset could also be used for other tasks such as fine-tuning language models, cross-lingual NLP tasks, machine translation, domain-specific text generation, and language-specific data analysis. **Is there anything about the composition of the dataset or the way it was collected and preprocessed/cleaned/labeled that might impact future uses? Is there anything a dataset consumer could do to mitigate these risks or harms?** Web-crawled content is over-represented with standard language varieties, impacting language model performance for minority languages. Language diversity in data is crucial to avoid bias, especially in encoding non-standard dialects, preventing the exclusion of demographic groups. Moreover, despite legal uncertainties in web-scraped data, we prioritize permissive licenses and privacy protection measures, acknowledging the challenges posed by personally identifiable information (PII) within large-scale datasets. Our ongoing efforts aim to address privacy concerns and contribute to a more inclusive linguistic dataset. **Are there tasks for which the dataset should not be used?** - #### Distribution **Will the dataset be distributed to third parties outside of the entity on behalf of which the dataset was created? If so, please provide a description.** The dataset will not be released or distributed to third parties. Any related question to distribution is omitted in this section. #### Maintenance **Who will be supporting/hosting/maintaining the dataset?** The dataset will be hosted by the Language Technologies unit (LangTech) of the Barcelona Supercomputing Center (BSC). The team will ensure regular updates and monitor the dataset for any issues related to content integrity, legal compliance, and bias for the sources they are responsible for. **How can the owner/curator/manager of the dataset be contacted?** The data owner may be contacted with the email address langtech@bsc.es. **Will the dataset be updated?** The dataset will not be updated. **If the dataset relates to people, are there applicable limits on the retention of the data associated with the instances? If so, please describe these limits and explain how they will be enforced.** The dataset does not keep sensitive data that could allow direct identification of individuals, apart from the data that is publicly available in web-sourced content. Due to the sheer volume and diversity of web data, it is not feasible to notify individuals or manage data retention on an individual basis. However, efforts are made to mitigate the risks associated with sensitive information through pre-processing and filtering to remove identifiable or harmful content. Despite these measures, vigilance is maintained to address potential privacy and ethical issues. **Will older versions of the dataset continue to be supported/hosted/maintained? If so, please describe how. If not, please describe how its obsolescence will be communicated to dataset consumers.** Since the dataset will not be updated, only the final version will be kept. **If others want to extend/augment/build on/contribute to the dataset, is there a mechanism for them to do so?** The dataset does not allow for external contributions.2b-instruct Finetuning Data
This instruction-tuned variant has been trained with a mixture of 276k English, Spanish, and Catalan multi-turn instructions gathered from open datasets:
| Dataset | ca | en | es |
|---|---|---|---|
| alpaca-cleaned | - | 50,000 | - |
| aya-dataset | - | 3,944 | 3,854 |
| CoQCat | 4,797 | - | - |
| databricks-dolly-15k | - | 15,011 | - |
| dolly-3k-ca | 3,232 | - | - |
| flores-instr | 1,994 | 1,994 | 3,988 |
| MentorCA | 7,122 | - | - |
| MentorES | - | - | 7,122 |
| no-robots | - | 9,499 | - |
| oasst-ca | 2,518 | - | - |
| oasst2 | 750 | 31,086 | 15,438 |
| open-orca | - | 50,000 | - |
| RagMultilingual | 16,043 | 14,997 | 11,263 |
| tower-blocks | - | 19,895 | 2,000 |
| Total | 36,456 | 196,426 | 43,665 |
Evaluation
Gold-standard benchmarks
Evaluation is done using the Language Model Evaluation Harness (Gao et al., 2024). We evaluate on a set of tasks taken from SpanishBench, CatalanBench, BasqueBench, and GalicianBench.
2B Instruct Model:
For the 2B instruct model, we evaluated tasks using the chat-template feature of the LM Evaluation Harness. We focused on tasks from human-generated or human-in-the-loop sources, ensuring high quality and accuracy. The model was evaluated in a 0-shot setting, where no prior examples were given to the model for prediction.
We observed ≈1.5% variances in performance for some tasks based on the version of the transformers library used and whether tensor parallelism was employed when loading the model. Replicating these results in other Harness implementations may yield different outcomes due to these factors. It’s important to note that gold-standard evaluations do not fully capture the model’s capabilities or potential, so caution is advised when interpreting the results.
2B Base Model:
The 2B base model was evaluated using the same benchmarks, including additional English tasks from the LM Evaluation Harness. We used a 5-shot setting for these evaluations, meaning that the model was provided with a few examples before making predictions. This slightly different setup allows for comparison between the instructed and non-instructed (base) versions of the model.
Similar issues with replicating results apply to the 2B base model, particularly variances in performance based on the library version and tensor parallelism settings.
Differences between 2B instruct and 2B base models:
- 2B instruct was evaluated in a 0-shot setting, where it receives no prior examples.
- 2B base was evaluated in a 5-shot setting, providing the model with examples before predicting.
- 2B instruct leverages
chat-templatefor instruction following tasks, making it more suited for conversational or instruction-driven tasks, while 2B base is a more general model without that specialization.
Spanish
| Category | Task | Metric | 2B Instruct | 2B Base |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Commonsense Reasoning | xstorycloze_es | acc | 62.34 | 64.92 |
| NLI | wnli_es | acc | 47.89 | 54.93 |
| xnli_es | acc | 47.03 | 44.98 | |
| Paraphrasing | paws_es | acc | 55.50 | 52.05 |
| QA | xquad_es | acc | 42.21 | 54.32 |
| Translation | flores_es | bleu | 20.27 | 11.46 |
Catalan
| Category | Task | Metric | 2B Instruct | 2B Base |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Commonsense Reasoning | copa_ca | acc | 70.40 | 68.80 |
| xstorycloze_ca | acc | 63.07 | 65.72 | |
| NLI | wnli_ca | acc | 52.11 | 56.34 |
| xnli_ca | acc | 51.69 | 48.07 | |
| Paraphrasing | parafraseja | acc | 61.88 | 58.55 |
| paws_ca | acc | 57.70 | 55.15 | |
| QA | arc_ca_easy | acc | 51.94 | 54.76 |
| arc_ca_challenge | acc | 29.52 | 30.55 | |
| openbookqa_ca | acc | 26.40 | 27.40 | |
| piqa_ca | acc | 62.89 | 62.89 | |
| siqa_ca | acc | 42.63 | 41.91 | |
| Translation | flores_ca | bleu | 24.48 | 14.70 |
Basque
| Category | Task | Metric | 2B Instruct | 2B Base |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Commonsense Reasoning | xcopa_eu | acc | 53.60 | 55.60 |
| xstorycloze_eu | acc | 56.39 | 57.64 | |
| NLI | wnli_eu | acc | 45.07 | 56.34 |
| xnli_eu | acc | 39.44 | 39.78 | |
| QA | eus_exams | acc | 25.35 | 23.72 |
| eus_proficiency | acc | 26.37 | 23.37 | |
| eus_trivia | acc | 26.24 | 27.58 | |
| Reading Comprehension | eus_reading | acc | 24.72 | 27.84 |
| Translation | flores_eu | bleu | 9.67 | 3.58 |
Galician
| Category | Task | Metric | 2B Instruct | 2B Base |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Paraphrasing | parafrases_gl | acc | 50.00 | 54.08 |
| paws_gl | acc | 52.20 | 53.30 | |
| QA | openbookqa_gl | acc | 33.20 | 30.80 |
| Translation | flores_gl | bleu | 22.39 | 12.86 |
English
| Category | Task | Metric | 2B Base |
|---|---|---|---|
| Commonsense Reasoning | copa | acc | 83.00 |
| xstorycloze_en | acc | 73.06 | |
| NLI | wnli | acc | 56.34 |
| xnli_en | acc | 47.35 | |
| Paraphrasing | paws * | acc | 55.95 |
| QA | arc_easy | acc | 74.07 |
| arc_challenge | acc | 37.63 | |
| openbookqa | acc | 28.00 | |
| piqa | acc | 74.86 | |
| social_iqa | acc | 46.62 | |
| squad_en ** | acc | 44.38 |
Ethical Considerations and Limitations
We examine the presence of undesired societal and cognitive biases in the 2B Base and 2B Instruct models using different benchmarks.
Societal Biases
- 2B Instruct: We use the BBQ dataset (Parrish et al., 2022) and the Regard dataset (Sheng et al., 2019). Results indicate moderate accuracies (between 0.5 and 0.6 depending on the social groups) in disambiguated settings, while the model performs poorly in ambiguous settings. These results suggest pervasive social biases that may affect task performance.
- 2B Base: Similar tests reveal inadequate accuracies in both ambiguous and disambiguated contexts, reflecting the presence of societal biases. These biases should be addressed in the post-training phases.
Cognitive Biases
- 2B Instruct: Positional effects in 0-shot settings and majority class bias in few-shot settings were analyzed. Moderate weak primacy effects were observed (a preference for earlier answers in multiple-choice questions), and we detected small majority class effects. This suggests some robustness against cognitive biases.
- 2B Base: We observed moderate to very strong primacy effects and significant majority class effects, implying that outputs are influenced by prompts and model settings.
Limitations and Next Steps
- Both models’ analyses are limited due to the scarcity of resources in many languages in the training data. Future work will expand analyses and testing.
- The observed biases are expected from models with limited instruction tuning. Developers should account for these biases and perform safety testing tailored to their specific applications.
Additional Information
Author
The Language Technologies Unit from Barcelona Supercomputing Center.
Contact
For further information, please send an email to langtech@bsc.es.
Copyright
Copyright© 2024 by Language Technologies Unit, Barcelona Supercomputing Center.
Funding
This work has been promoted and financed by the Government of Catalonia through the Aina Project.
This work is funded by the Ministerio para la Transformación Digital y de la Función Pública - Funded by EU – NextGenerationEU within the framework of ILENIA Project with reference 2022/TL22/00215337.
Acknowledgements
This project has benefited from the contributions of numerous teams and institutions, mainly through data contributions, knowledge transfer, or technical support.
- Catalonia: Thanks to Òmnium Cultural, Parlament de Catalunya, Institut d’Estudis Aranesos, Racó Català, Vilaweb, ACN, Nació Digital, El món, and Aquí Berguedà.
- National level: Special thanks to our ILENIA project partners: CENID, HiTZ, and CiTIUS. Also, thanks to the Spanish Senate and Congress, Fundación Dialnet, Fundación Elcano, and the Instituto Universitario de Sistemas Inteligentes y Aplicaciones Numéricas en Ingeniería (SIANI).
- International level: Gratitude to the Welsh government, DFKI, Occiglot project, and Common Crawl Foundation. Special thanks to the NVIDIA team, including Ignacio Sarasua, Adam Henryk Grzywaczewski, Oleg Sudakov, Sergio Perez, Miguel Martinez, Felipes Soares, and Meriem Bendris for their support.
Disclaimer
Be aware that the model may contain biases or other unintended distortions. Third-party developers deploying systems or using the model must take responsibility for mitigating risks and ensuring compliance with AI regulations. The Barcelona Supercomputing Center is not liable for outcomes resulting from third-party use.
Citation
Technical report and paper coming soon.
License
Model Index
| Model | Base | Instruct |
|---|---|---|
| 2B | Link | Link |
| 7B | Link | Link |
| 40B | WiP | WiP |