Web search
September 24, 2025
A new web search API is now available in Ollama. Ollama provides a generous free tier of web searches for individuals to use, and higher rate limits are available via Ollama’s cloud.
This web search capability can augment models with the latest information from the web to reduce hallucinations and improve accuracy.
Web search is provided as a REST API with deeper tool integrations in Ollama’s Python and JavaScript libraries. This also enables models such as OpenAI’s gpt-oss models to conduct long-running research tasks.
Get started
Create an API key from your Ollama account.
export OLLAMA_API_KEY="your_api_key"
cURL
curl https://ollama.com/api/web_search \
--header "Authorization: Bearer $OLLAMA_API_KEY" \
-d '{
"query": "what is ollama?"
}'
Example output
{
"results": [
{
"title": "Ollama",
"url": "https://ollama.com/",
"content": "Cloud models are now available..."
},
{
"title": "What is Ollama? Introduction to the AI model management tool",
"url": "https://www.hostinger.com/tutorials/what-is-ollama",
"content": "Ariffud M. 6min Read..."
},
{
"title": "Ollama Explained: Transforming AI Accessibility and Language ...",
"url": "https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/artificial-intelligence/ollama-explained-transforming-ai-accessibility-and-language-processing/",
"content": "Data Science Data Science Projects Data Analysis..."
}
]
}
Python
Install and run Ollama’s Python library
pip install 'ollama>=0.6.0'
Then make a request using ollama.web_search:
import ollama
response = ollama.web_search("What is Ollama?")
print(response)
Example output
results = [
{
"title": "Ollama",
"url": "https://ollama.com/",
"content": "Cloud models are now available in Ollama..."
},
{
"title": "What is Ollama? Features, Pricing, and Use Cases - Walturn",
"url": "https://www.walturn.com/insights/what-is-ollama-features-pricing-and-use-cases",
"content": "Our services..."
},
{
"title": "Complete Ollama Guide: Installation, Usage & Code Examples",
"url": "https://collabnix.com/complete-ollama-guide-installation-usage-code-examples",
"content": "Join our Discord Server..."
}
]
JavaScript
Install and run Ollama’s JavaScript library
npm install 'ollama@>=0.6.0'
import { Ollama } from "ollama";
const client = new Ollama();
const results = await client.webSearch({ query: "what is ollama?" });
console.log(JSON.stringify(results, null, 2));
Example output
{
"results": [
{
"title": "Ollama",
"url": "https://ollama.com/",
"content": "Cloud models are now available..."
},
{
"title": "What is Ollama? Introduction to the AI model management tool",
"url": "https://www.hostinger.com/tutorials/what-is-ollama",
"content": "Ollama is an open-source tool..."
},
{
"title": "Ollama Explained: Transforming AI Accessibility and Language Processing",
"url": "https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/artificial-intelligence/ollama-explained-transforming-ai-accessibility-and-language-processing/",
"content": "Ollama is a groundbreaking..."
}
]
}
Building a search agent
Use Ollama’s web search as a tool to build a mini search agent.
The example uses Alibaba’s Qwen 3 model with 4B parameters.
ollama pull qwen3:4b
from ollama import chat, web_fetch, web_search
available_tools = {'web_search': web_search, 'web_fetch': web_fetch}
messages = [{'role': 'user', 'content': "what is ollama's new engine"}]
while True:
response = chat(
model='qwen3:4b',
messages=messages,
tools=[web_search, web_fetch],
think=True
)
if response.message.thinking:
print('Thinking: ', response.message.thinking)
if response.message.content:
print('Content: ', response.message.content)
messages.append(response.message)
if response.message.tool_calls:
print('Tool calls: ', response.message.tool_calls)
for tool_call in response.message.tool_calls:
function_to_call = available_tools.get(tool_call.function.name)
if function_to_call:
args = tool_call.function.arguments
result = function_to_call(**args)
print('Result: ', str(result)[:200]+'...')
# Result is truncated for limited context lengths
messages.append({'role': 'tool', 'content': str(result)[:2000 * 4], 'tool_name': tool_call.function.name})
else:
messages.append({'role': 'tool', 'content': f'Tool {tool_call.function.name} not found', 'tool_name': tool_call.function.name})
else:
break
Result
Thinking: Okay, the user is asking about Ollama's new engine. I need to figure out what they're referring to. Ollama is a company that develops large language models, so maybe they've released a new model or an updated version of their existing engine...
Tool calls: [ToolCall(function=Function(name='web_search', arguments={'max_results': 3, 'query': 'Ollama new engine'}))]
Result: results=[WebSearchResult(content='# New model scheduling\n\n## September 23, 2025\n\nOllama now includes a significantly improved model scheduling system. Ahead of running a model, Ollama’s new engine...
Thinking: Okay, the user asked about Ollama's new engine. Let me look at the search results.
First result is from September 23, 2025, talking about new model scheduling. It mentions improved memory management, reduced crashes, better GPU utilization, and multi-GPU performance. Examples show speed improvements and accurate memory reporting. Supported models include gemma3, llama4, qwen3, etc...
Content: Ollama has introduced two key updates to its engine, both released in 2025:
1. **Enhanced Model Scheduling (September 23, 2025)**
- **Precision Memory Management**: Exact memory allocation reduces out-of-memory crashes and optimizes GPU utilization.
- **Performance Gains**: Examples show significant speed improvements (e.g., 85.54 tokens/s vs 52.02 tokens/s) and full GPU layer utilization.
- **Multi-GPU Support**: Improved efficiency across multiple GPUs, with accurate memory reporting via tools like `nvidia-smi`.
- **Supported Models**: Includes `gemma3`, `llama4`, `qwen3`, `mistral-small3.2`, and more.
2. **Multimodal Engine (May 15, 2025)**
- **Vision Support**: First-class support for vision models, including `llama4:scout` (109B parameters), `gemma3`, `qwen2.5vl`, and `mistral-small3.1`.
- **Multimodal Tasks**: Examples include identifying animals in multiple images, answering location-based questions from videos, and document scanning.
These updates highlight Ollama's focus on efficiency, performance, and expanded capabilities for both text and vision tasks.
Recommended models:
These models have great tool-use capabilities and are able to have multi-turn interactions with the user and tools to get to a final result.
qwen3gpt-oss
Recommended cloud models:
qwen3:480b-cloudgpt-oss:120b-clouddeepseek-v3.1-cloud
The web_search and web_fetch tools can return thousands of tokens. It is recommended to increase the context length of the model to ~32000 tokens for reasonable performance. Search agents work best with full context length.
Fetching page results
To fetch individual pages (e.g. when a user provides a url in the prompt), use the new web fetch API.
Python library
from ollama import web_fetch
result = web_fetch('https://ollama.com')
print(result)
Result
WebFetchResponse(
title='Ollama',
content='[Cloud models](https://ollama.com/blog/cloud-models) are now available in Ollama\n\n**Chat & build
with open models**\n\n[Download](https://ollama.com/download) [Explore
models](https://ollama.com/models)\n\nAvailable for macOS, Windows, and Linux',
links=['https://ollama.com/', 'https://ollama.com/models', 'https://github.com/ollama/ollama']
)
Example Python code is available on GitHub.
JavaScript library
import { Ollama } from "ollama";
const client = new Ollama();
const fetchResult = await client.webFetch({ url: "https://ollama.com" });
console.log(JSON.stringify(fetchResult, null, 2));
Result
{
"title": "Ollama",
"content": "[Cloud models](https://ollama.com/blog/cloud-models) are now available in Ollama...",
"links": [
"https://ollama.com/",
"https://ollama.com/models",
"https://github.com/ollama/ollama"
]
}
Example JavaScript code is available on GitHub.
cURL
curl --request POST \
--url https://ollama.com/api/web_fetch \
--header "Authorization: Bearer $OLLAMA_API_KEY" \
--header 'Content-Type: application/json' \
--data '{
"url": "ollama.com"
}'
Result
{
"title": "Ollama",
"content": "[Cloud models](https://ollama.com/blog/cloud-models) are now available in Ollama...",
"links": [
"http://ollama.com/",
"http://ollama.com/models",
"https://github.com/ollama/ollama"
]
}
Integrations
MCP Server (Model Context Protocol server)
You can enable web search in any MCP client through the Python MCP server.
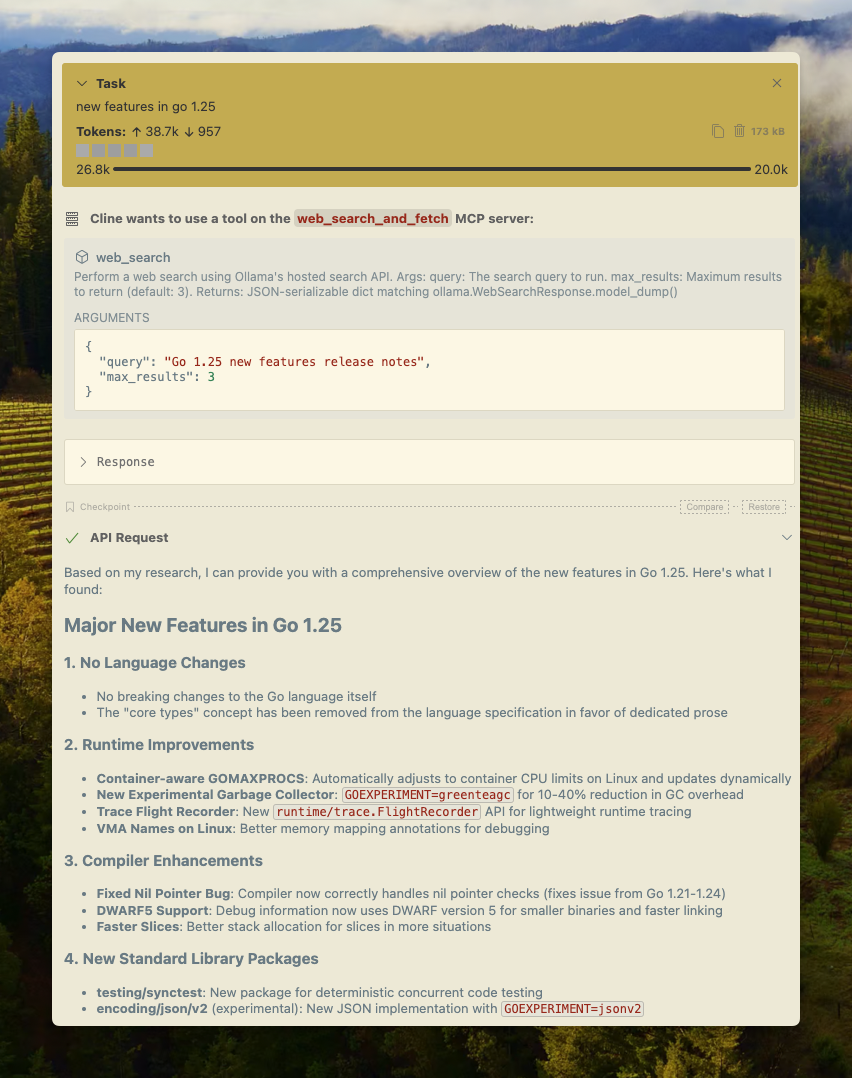
Cline
To integrate with Cline, configure MCP servers in its settings.
- Manage MCP Servers > Configure MCP Servers > Add the configuration below
{
"mcpServers": {
"web_search_and_fetch": {
"type": "stdio",
"command": "uv",
"args": ["run", "path/to/web-search-mcp.py"],
"env": { "OLLAMA_API_KEY": "your_api_key_here" }
}
}
}
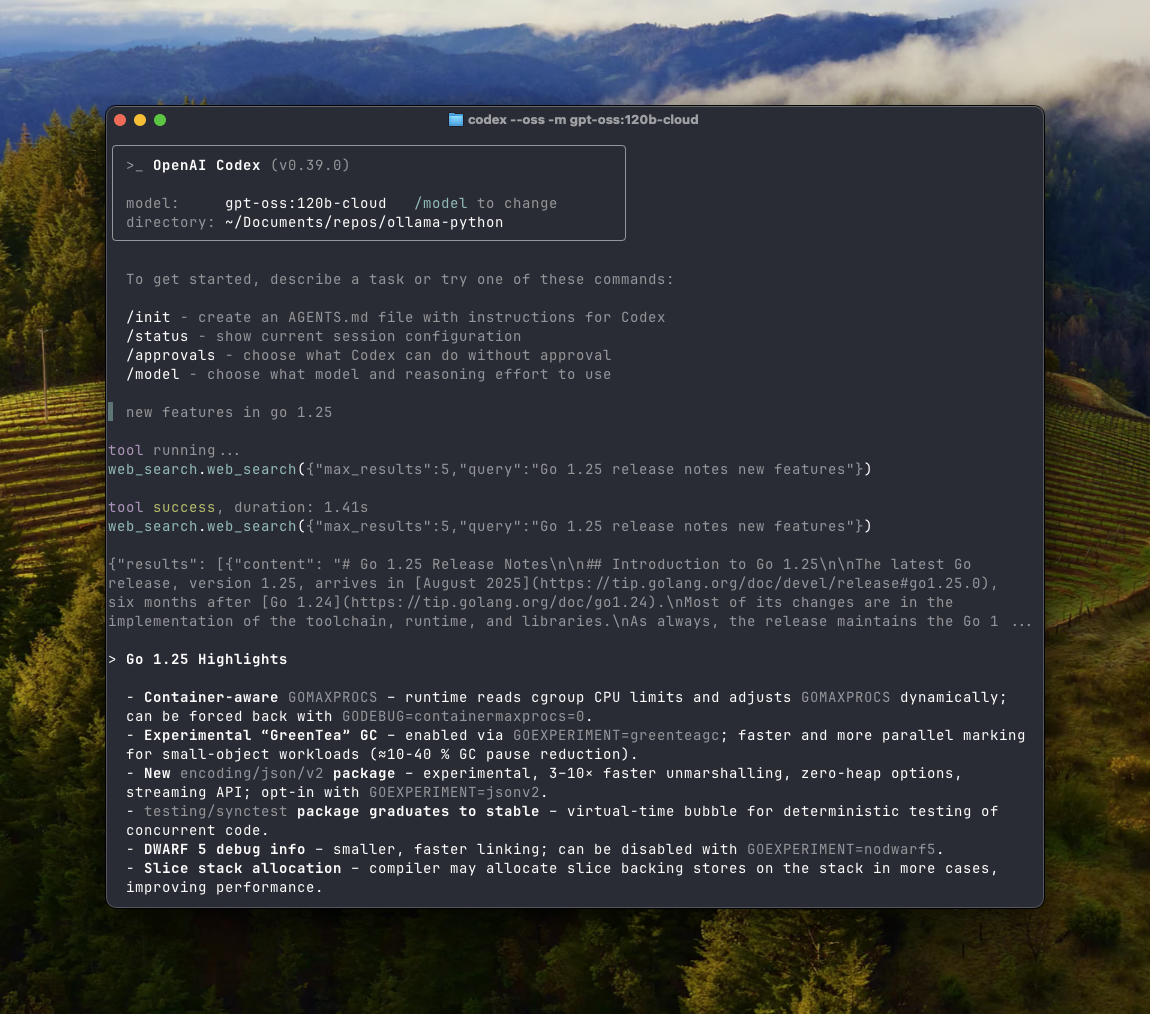
Codex
Add the following configuration to ~/.codex/config.toml
[mcp_servers.web_search]
command = "uv"
args = ["run", "path/to/web-search-mcp.py"]
env = { "OLLAMA_API_KEY" = "your_api_key_here" }
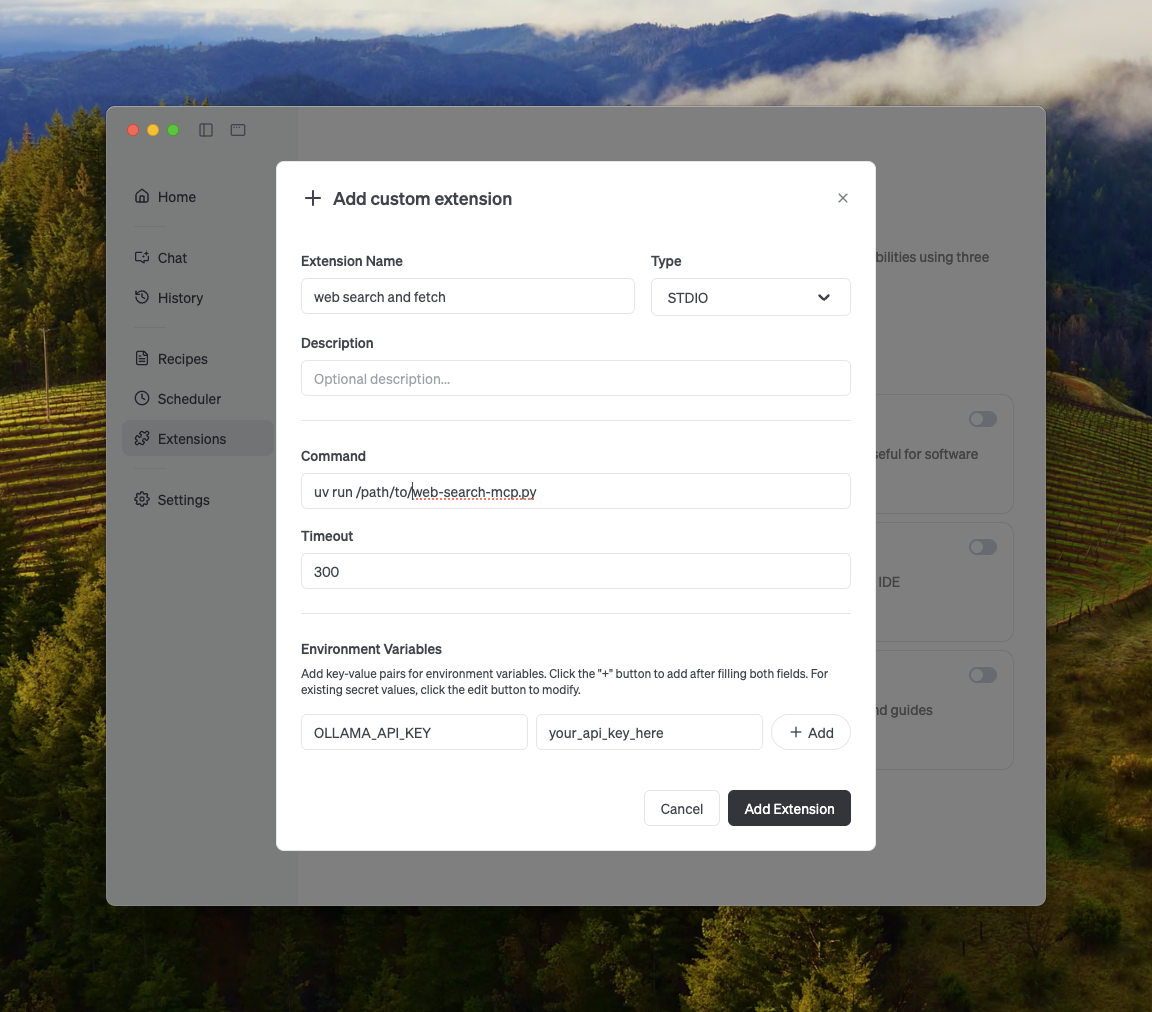
Goose
You can integrate with Ollama via Goose’s extensions.
Get started
Web search is included with a free Ollama account, with much higher rate limits available by upgrading your Ollama subscription.
To get started, sign up for an Ollama account!